Data visualisation
Bio300B Lecture 4
Institutt for biovitenskap, UiB
8 September 2025
Data visualisation
- A picture is worth a thousand words
- Tell a story with figures
- Avoid common mistakes
“reflect the data, tell a story, and look professional” Wilke
ggplot2
- one of at least three schemes for graphics in R
- part of tidyverse
A system for ‘declaratively’ creating graphics, based on “The Grammar of Graphics”.
You provide the data, tell ‘ggplot2’ how to map variables to aesthetics, what graphical primitives to use, it takes care of the details.
ggplot in action
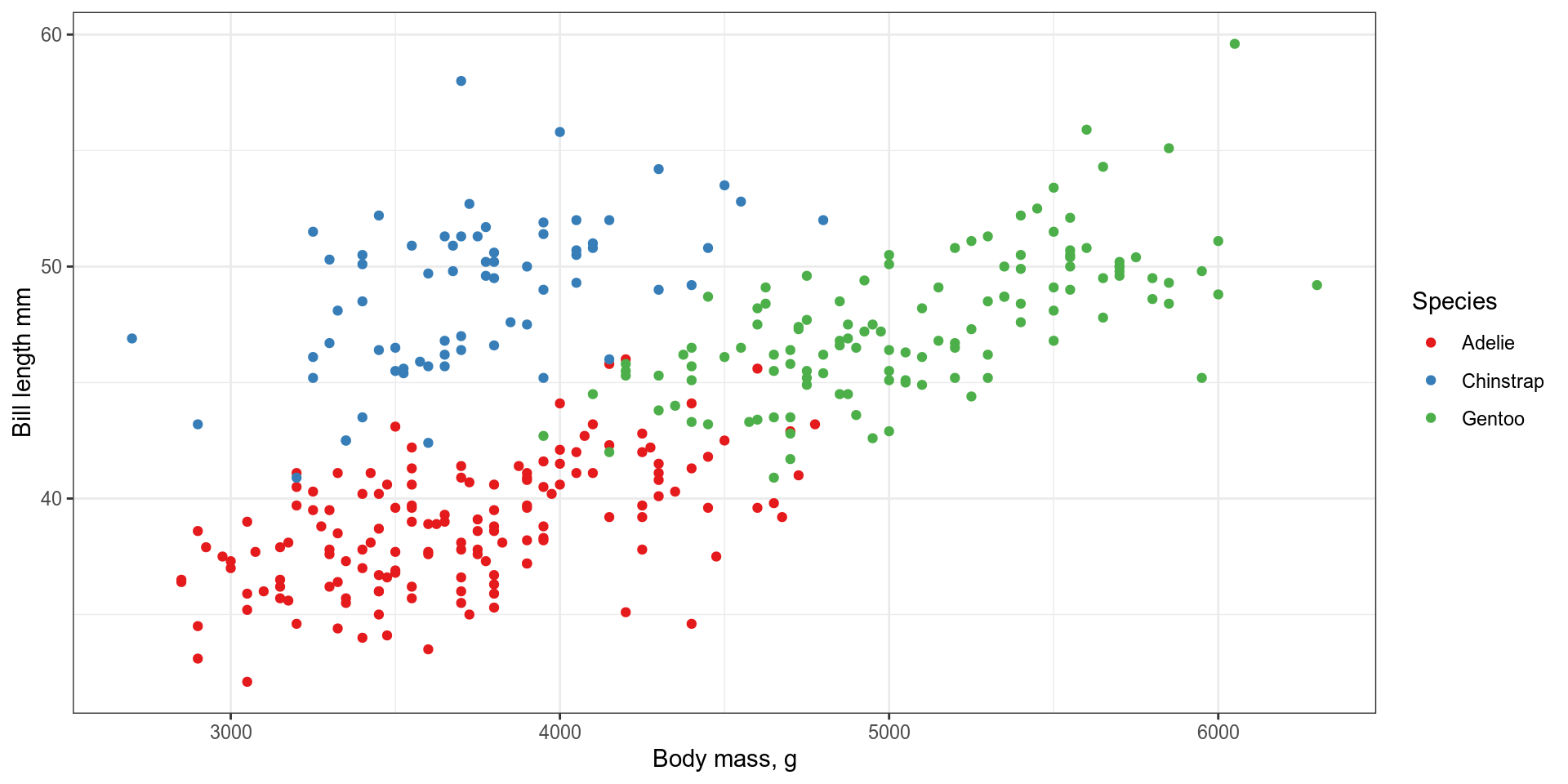
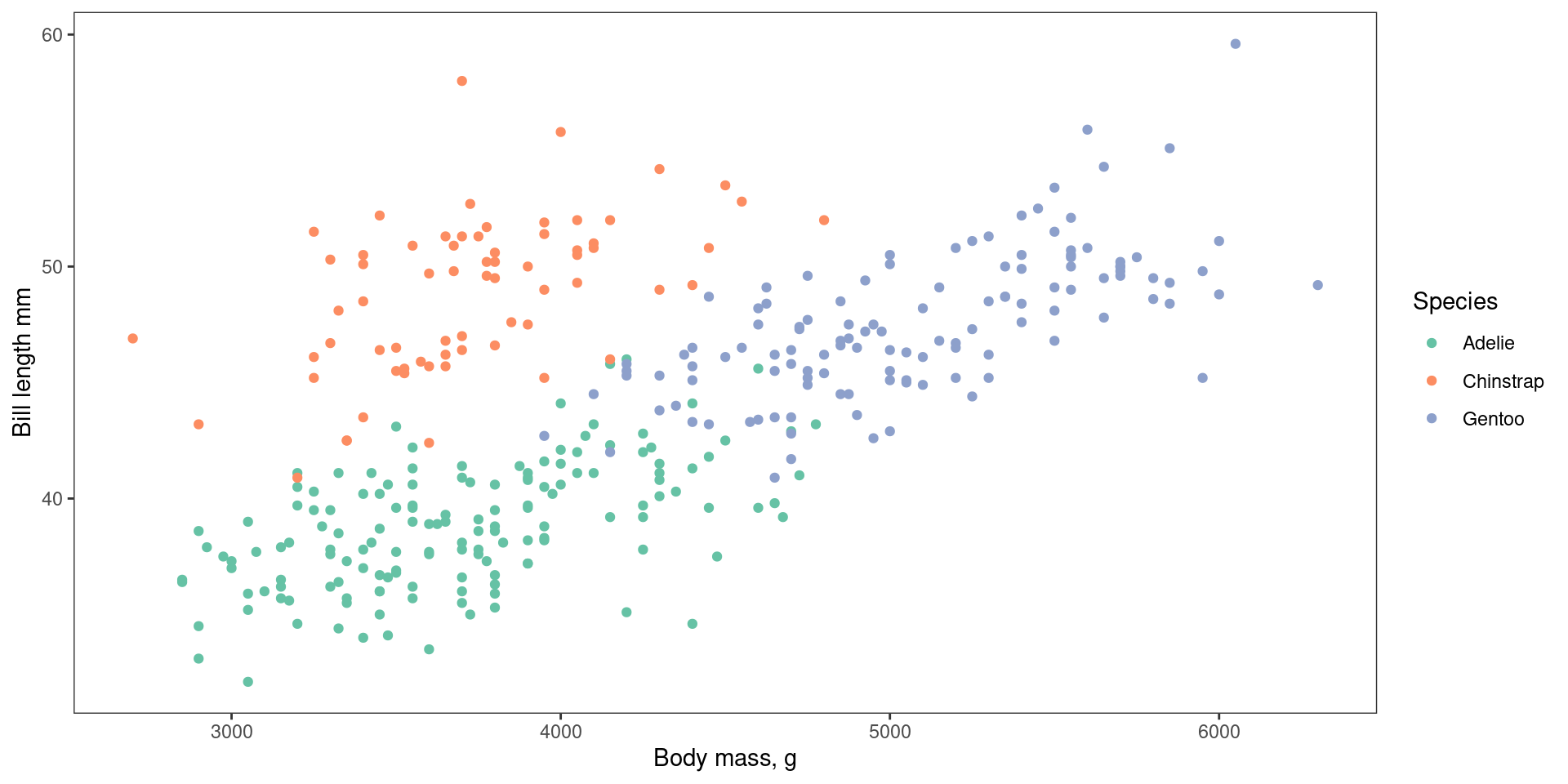
plot <- ggplot(data = penguins, # Data
mapping = aes( # Aesthetics
x = body_mass_g,
y = bill_length_mm,
colour = species)) +
geom_point() + # Geometries
scale_colour_brewer(palette = "Set2") + # scales
labs(x = "Body mass, g", # labels
y = "Bill length mm",
colour = "Species") +
theme_bw() # themes
# Also facets
plotggplot in action
Data
Tibble or data frame with data to be plotted.
Tidy data
Can process data within ggplot but usually best to do it first
Can add data to the whole plot or to individual geoms
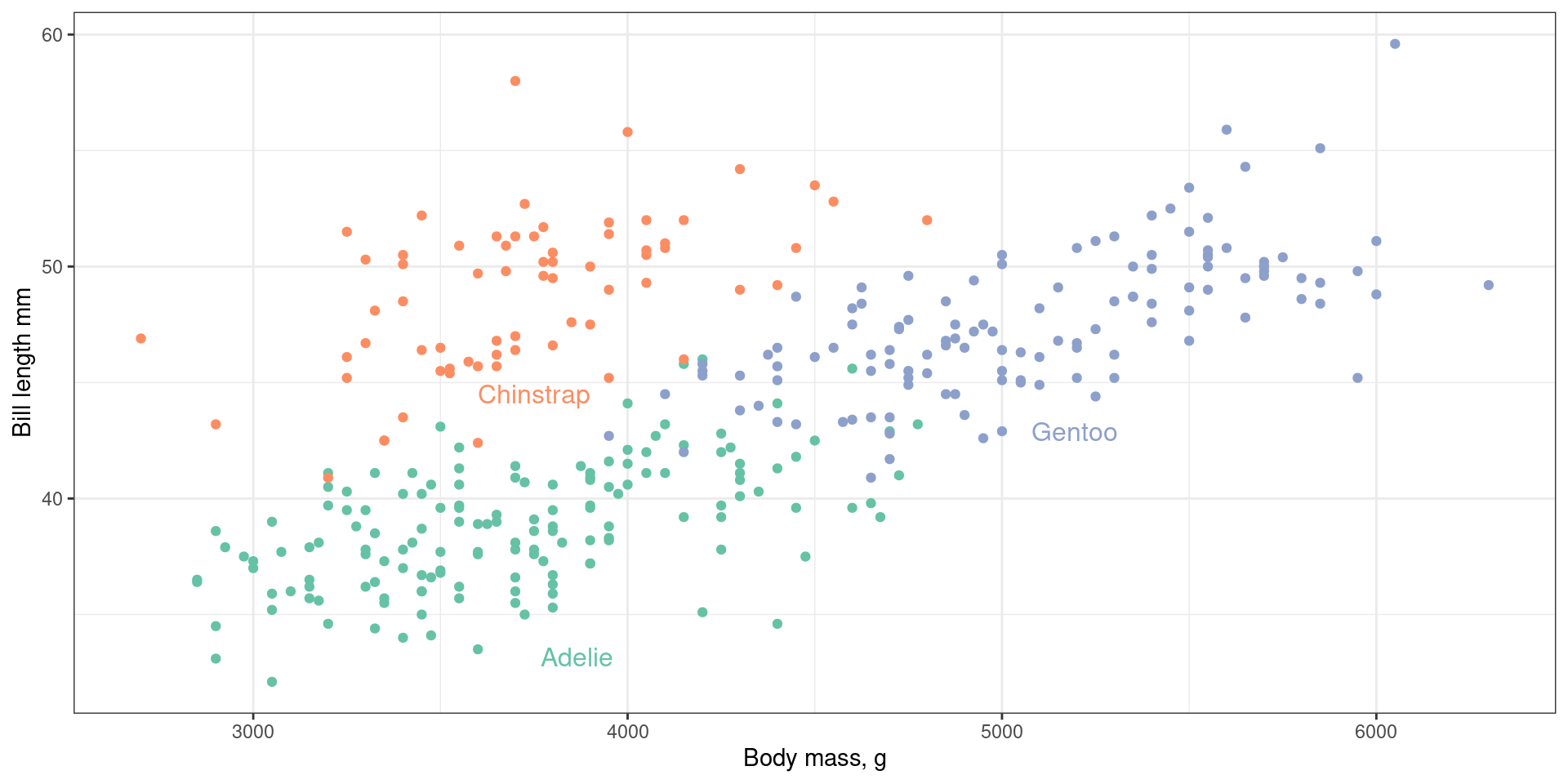
penguin_summary <- penguins |> group_by(species) |> summarise(body_mass_g = mean(body_mass_g, na.rm = TRUE), bill_length_mm = mean(bill_length_mm, na.rm = TRUE) )
ggplot(penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point() +
geom_text(aes(label = species), data = penguin_summary, colour = "black")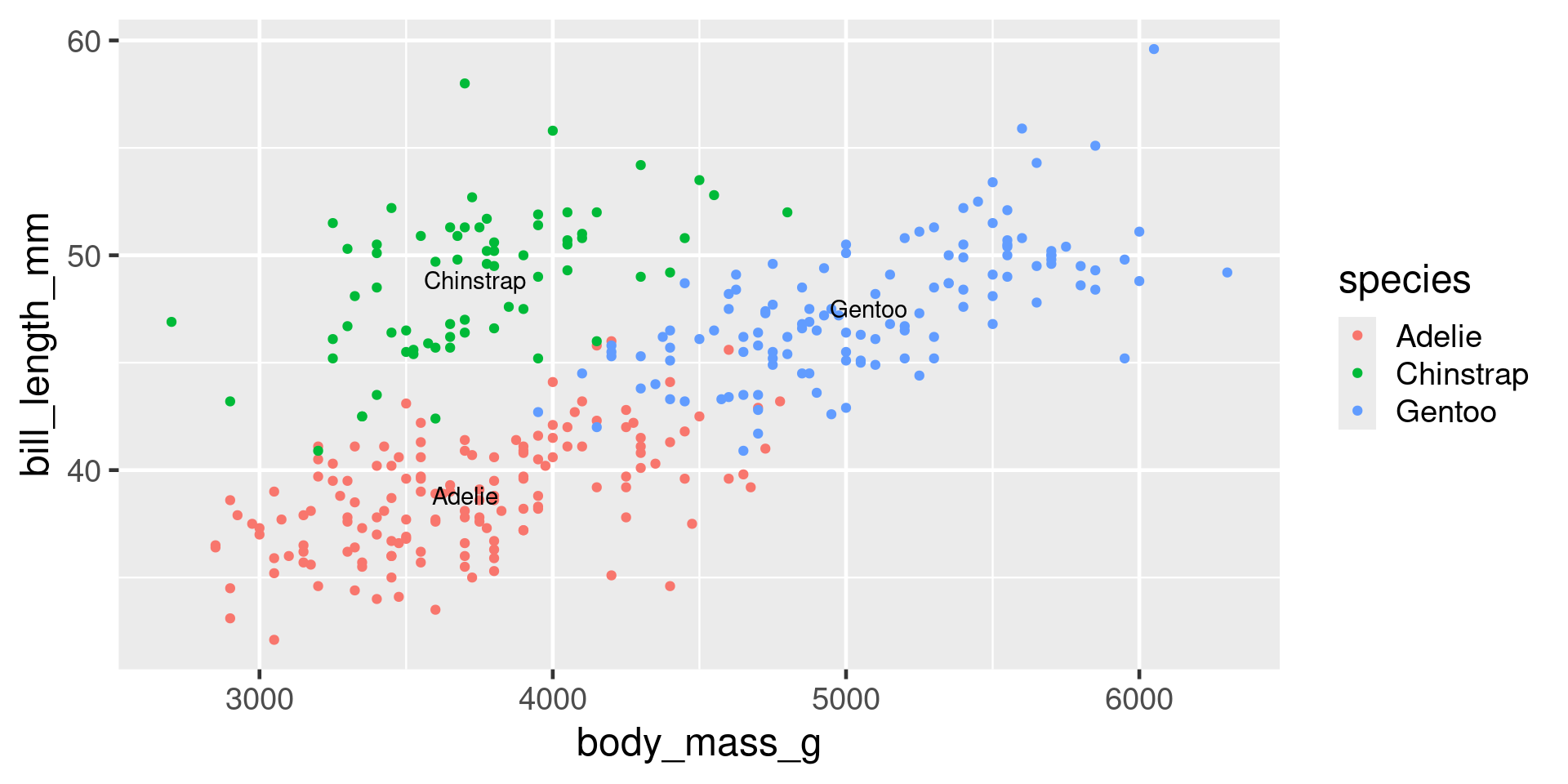
Aesthetics
mapping specifies which variables in the data should be mapped onto which aesthetics with aes()
Each geom takes different aesthetics
Common aesthetics
- x, y
- fill, colour, alpha
- shape, size
- linetype, linewidth
- group
Setting vs mapping
geoms
Use different geoms for different plot types
Important geoms
geom_point()geom_boxplot()geom_histogram()geom_smooth()geom_line()geom_text()
Many geoms, some in extra packages
Geoms to show distributions
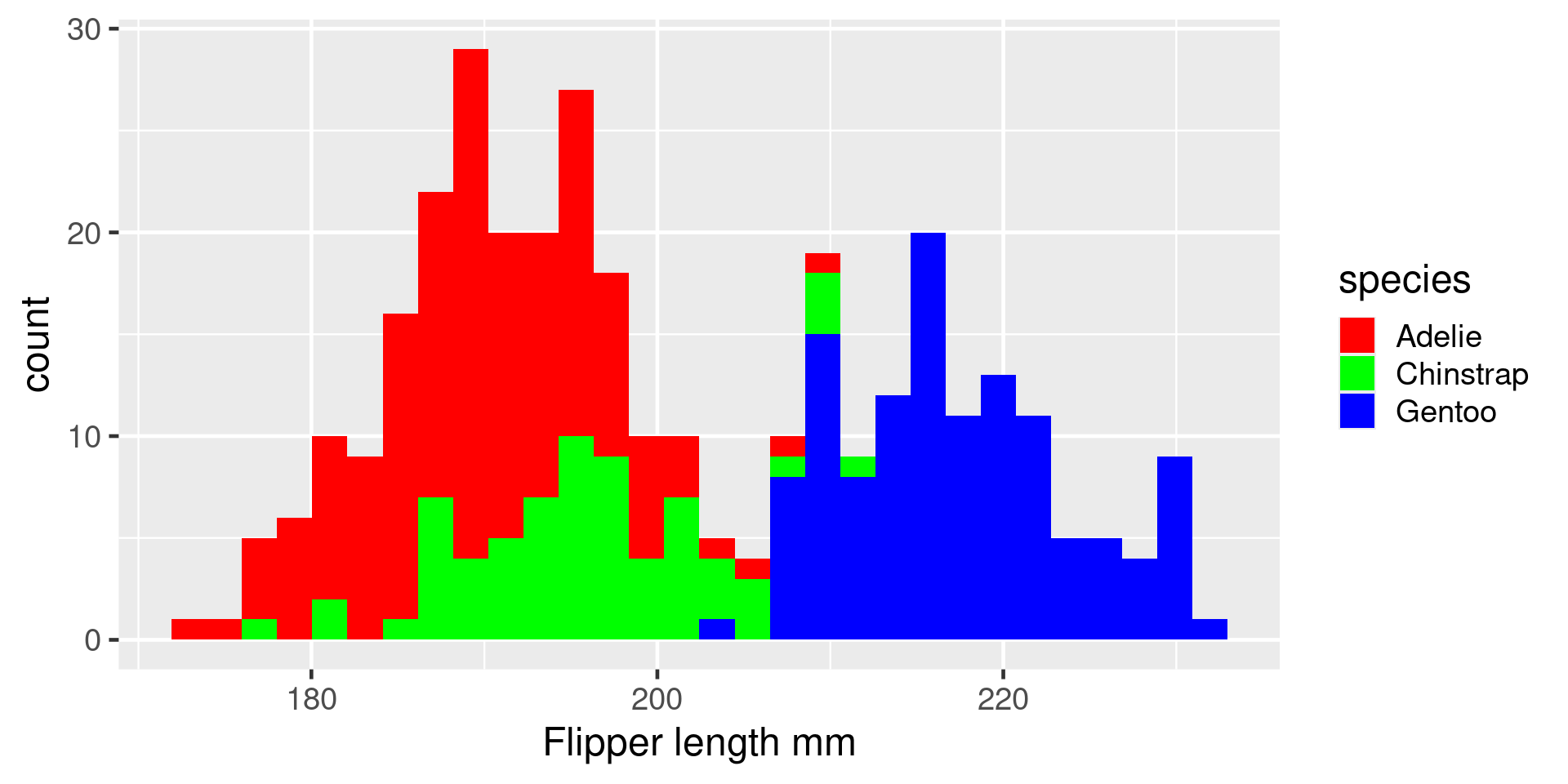
Histogram
Count how many observations in each bin
Critical question - how many bins? Set with bins argument
viewof bins = Inputs.range(
[ 1, 50 ],
{ label: "Number of bins", step: 1, value: 30 },
)
viewof measure2 = Inputs.select(
[ "flipper_length_mm", "bill_length_mm", "bill_depth_mm", "body_mass_g" ],
{ label: "Measure" }
);
viewof species = Inputs.select(
[ "Adelie", "Chinstrap", "Gentoo" ],
{ label: "Species" }
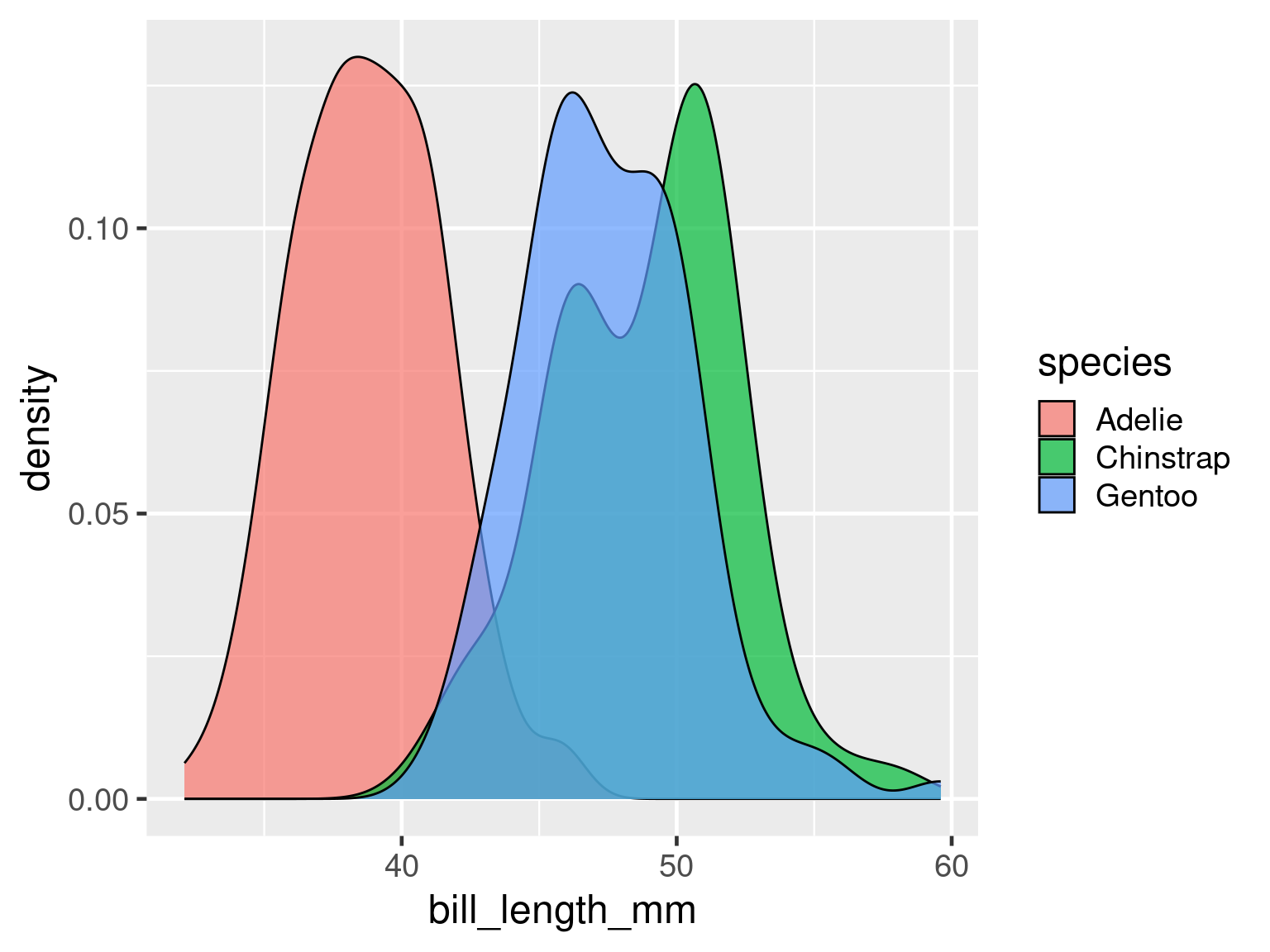
);Density
Smoothed histograms
adjust argument adjusts bandwidth to control how smooth
Geoms to show many distributions
base <- ggplot(penguins, aes(x = species, y = flipper_length_mm))
p_prange <- base + stat_summary(fun = "mean", geom = "col")
p_box <- base + geom_boxplot(aes(fill = species))
p_vio <- base + geom_violin(aes(fill = species))
p_jit <- base + geom_jitter(aes(colour = species))
library(ggbeeswarm)
p_quasi <- base + geom_quasirandom(aes(colour = species))
p_quasi2 <- base + geom_violin(aes(fill = species), alpha = 0.3) +
geom_quasirandom(aes(colour = species))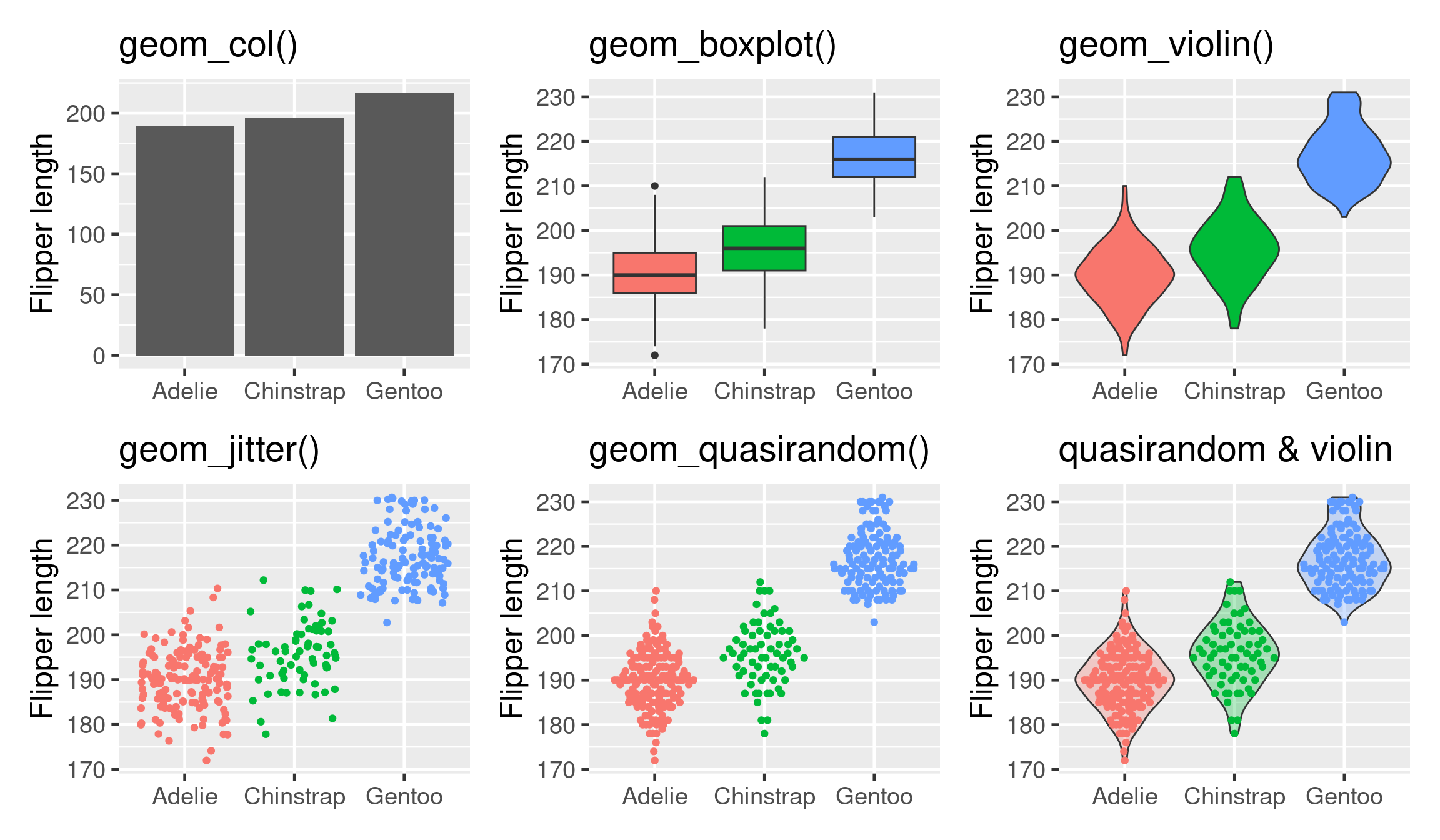
Boxplots can mislead
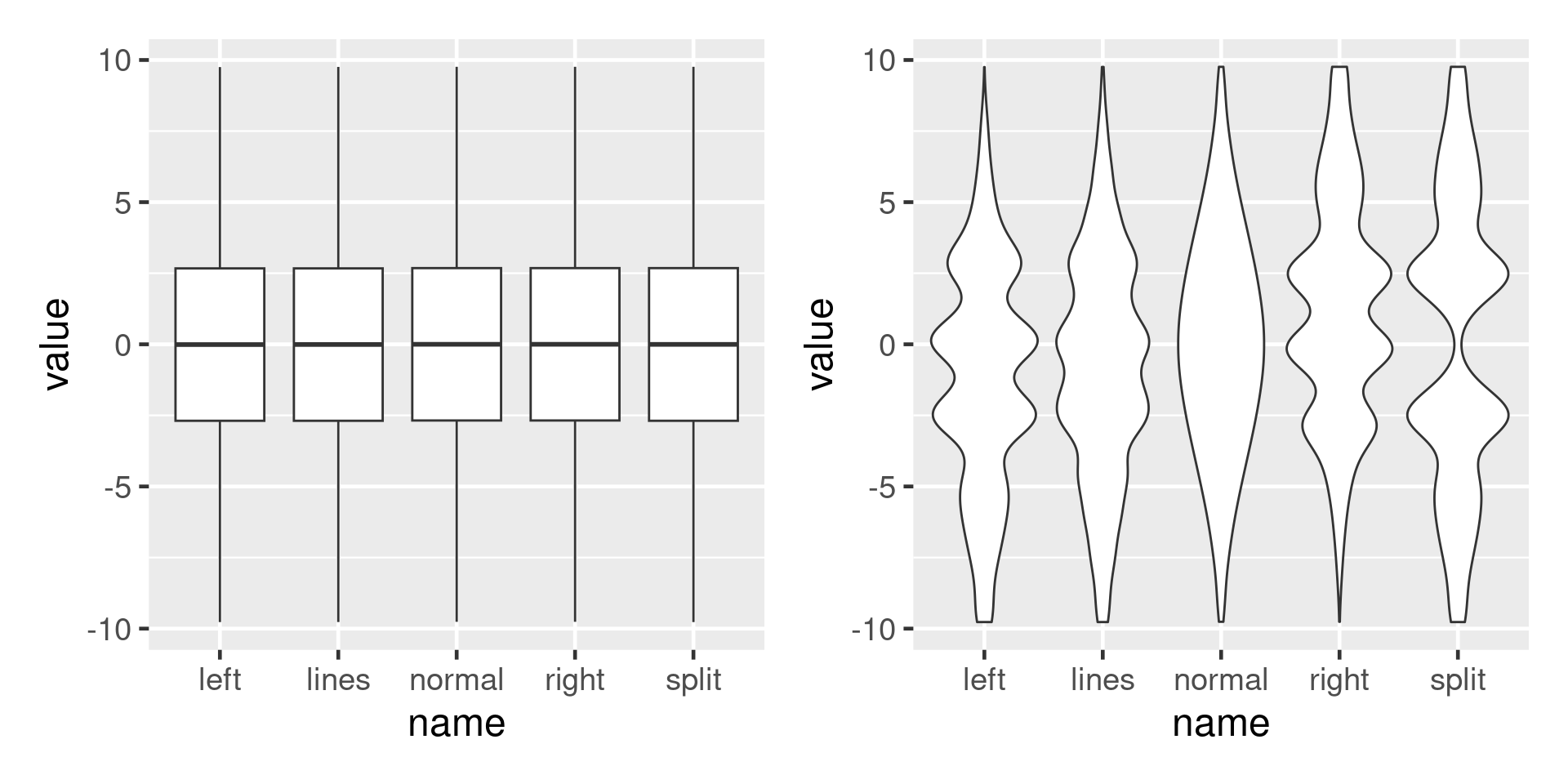
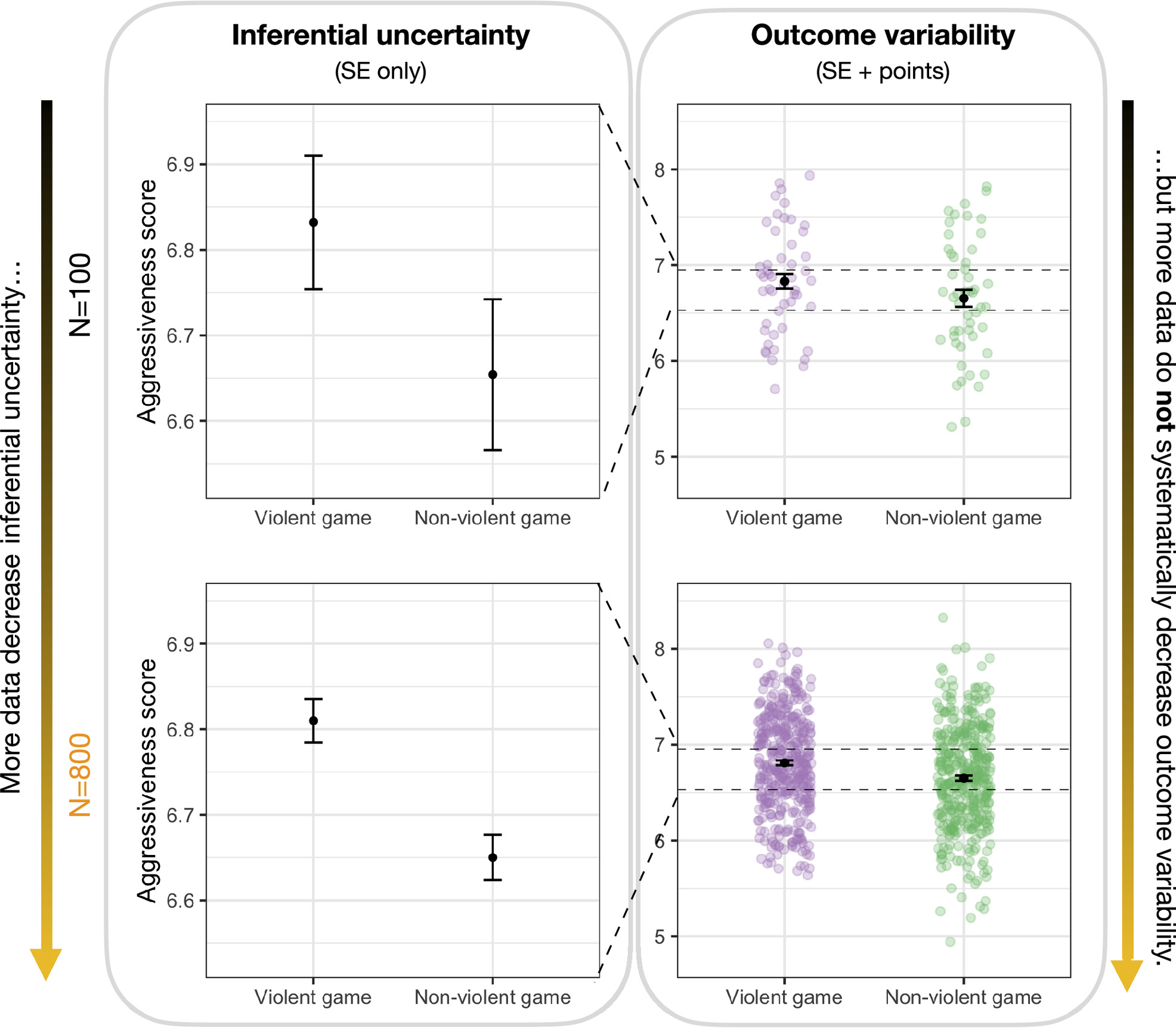
Show the raw data
geoms for scatterplots
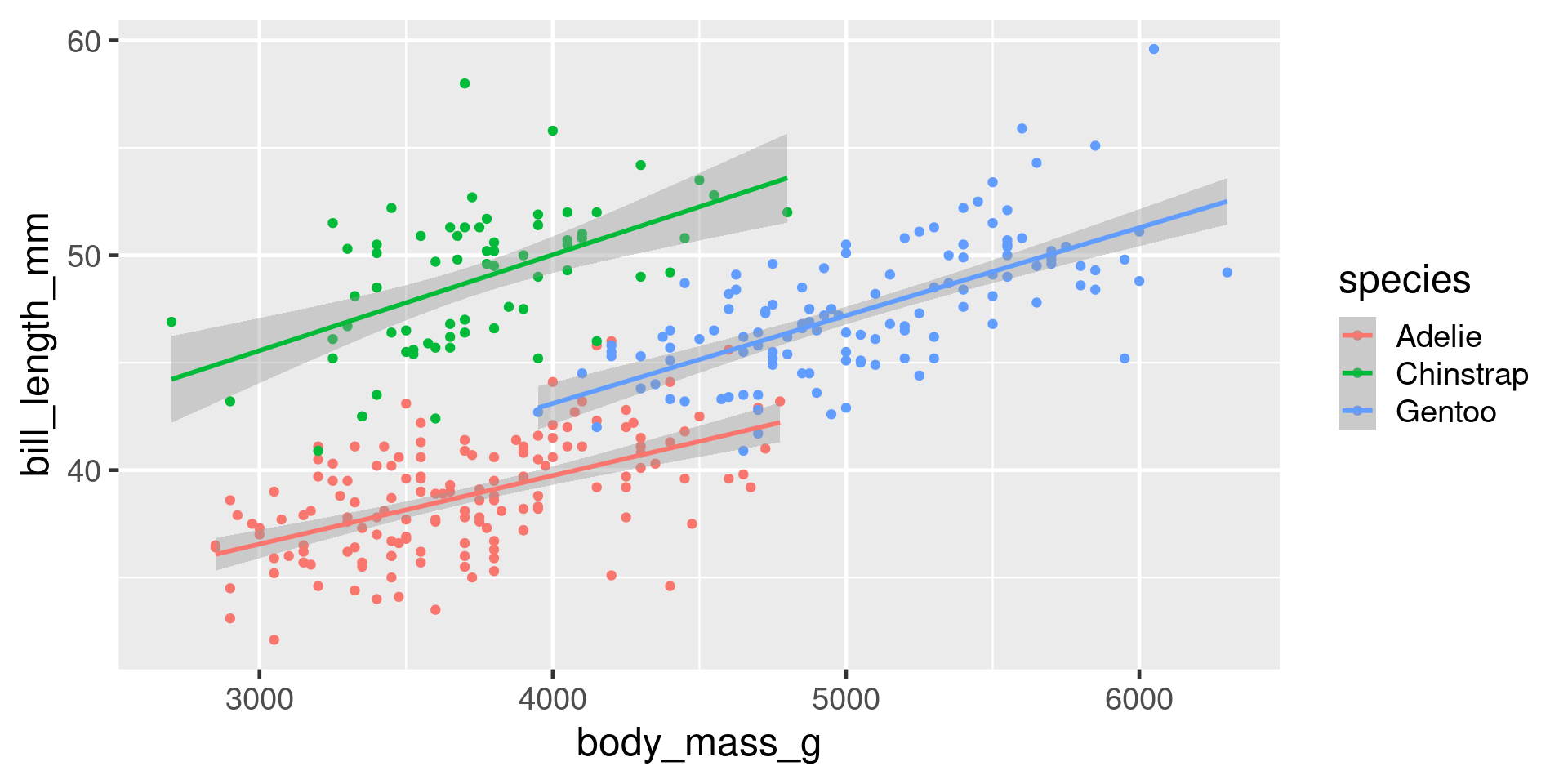
geom_line()- join observations from left-rightgeom_path()- join observations from first to last in data
Scales
Control how
- variables are mapped onto the aesthetics
- axes breaks
All called scale_aesthetic_description
scale_x_log()scale_y_reverse()scale_colour_viridis_c()scale_shape_manual()
Labels
- plot, axis and legend titles
Facets
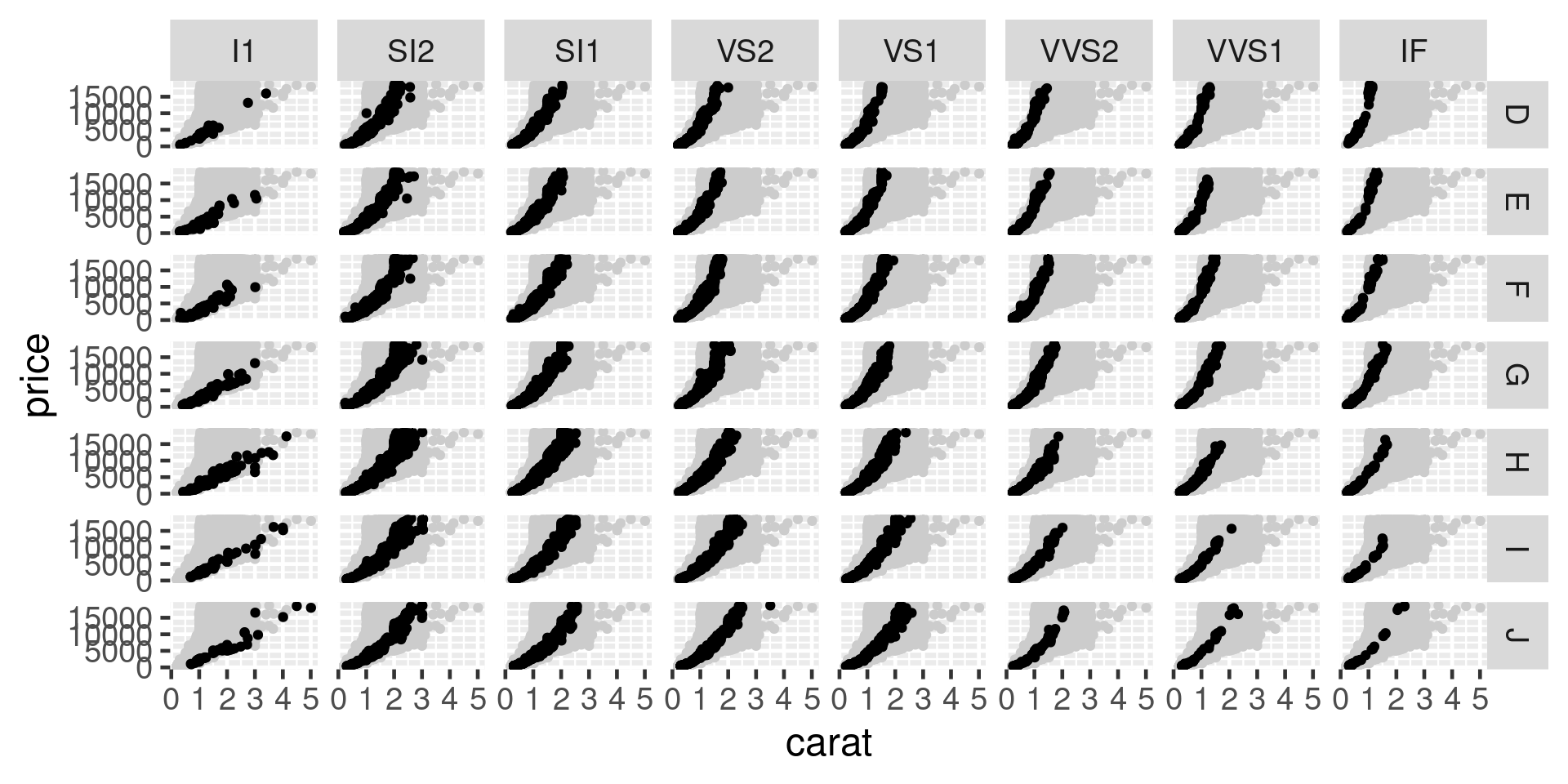
Split data into separate panels.
facet_grid() for two dimensional arrays of subplots

Themes
Change how non-data elements of the plot look
Entire themes
Themes
Can also change individual elements
Removing elements
Colour & fills
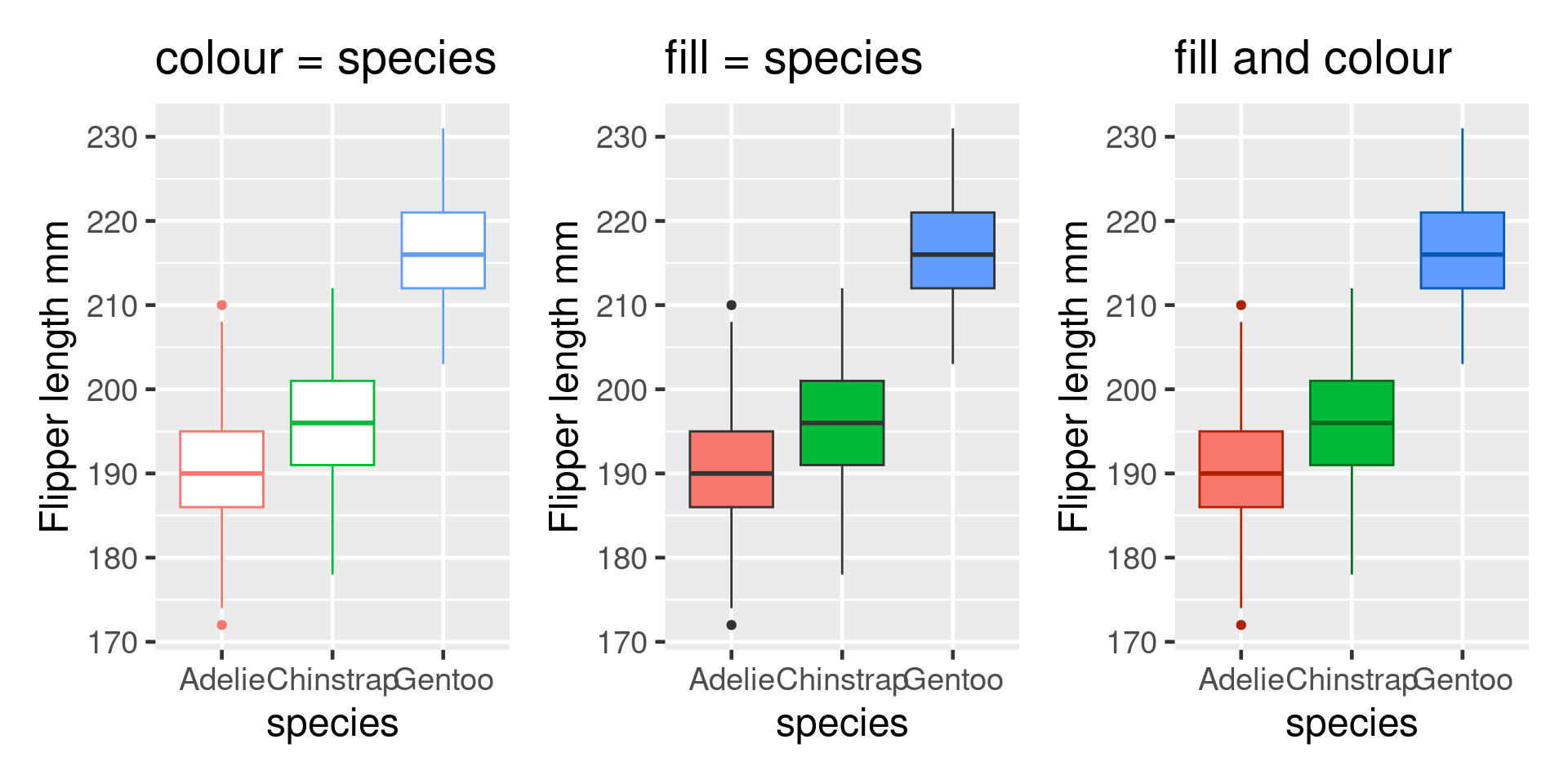
Avoid primary colours
Colour deficient vision
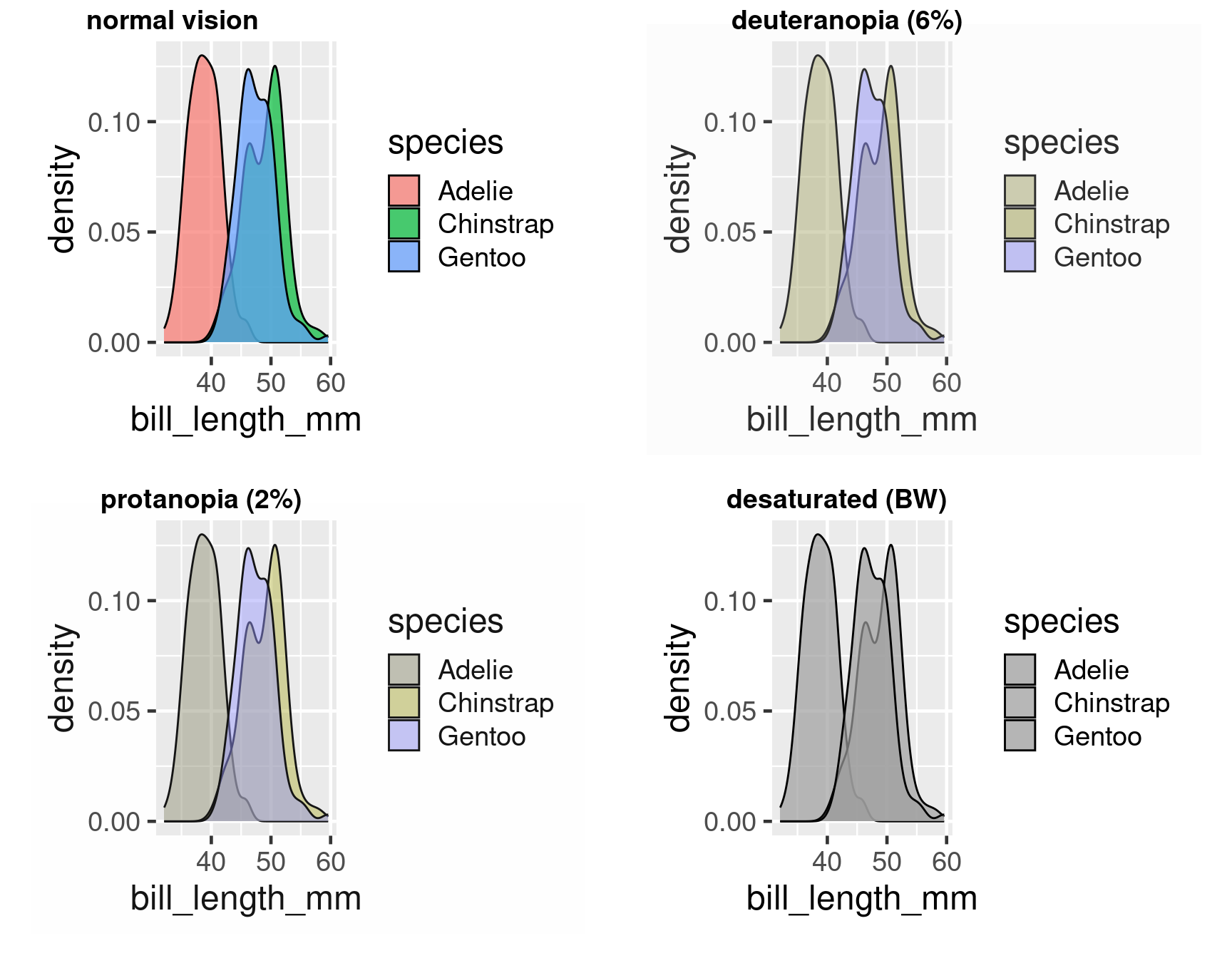
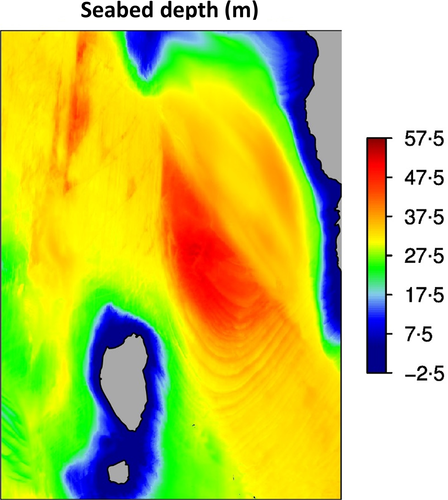
#End rainbow
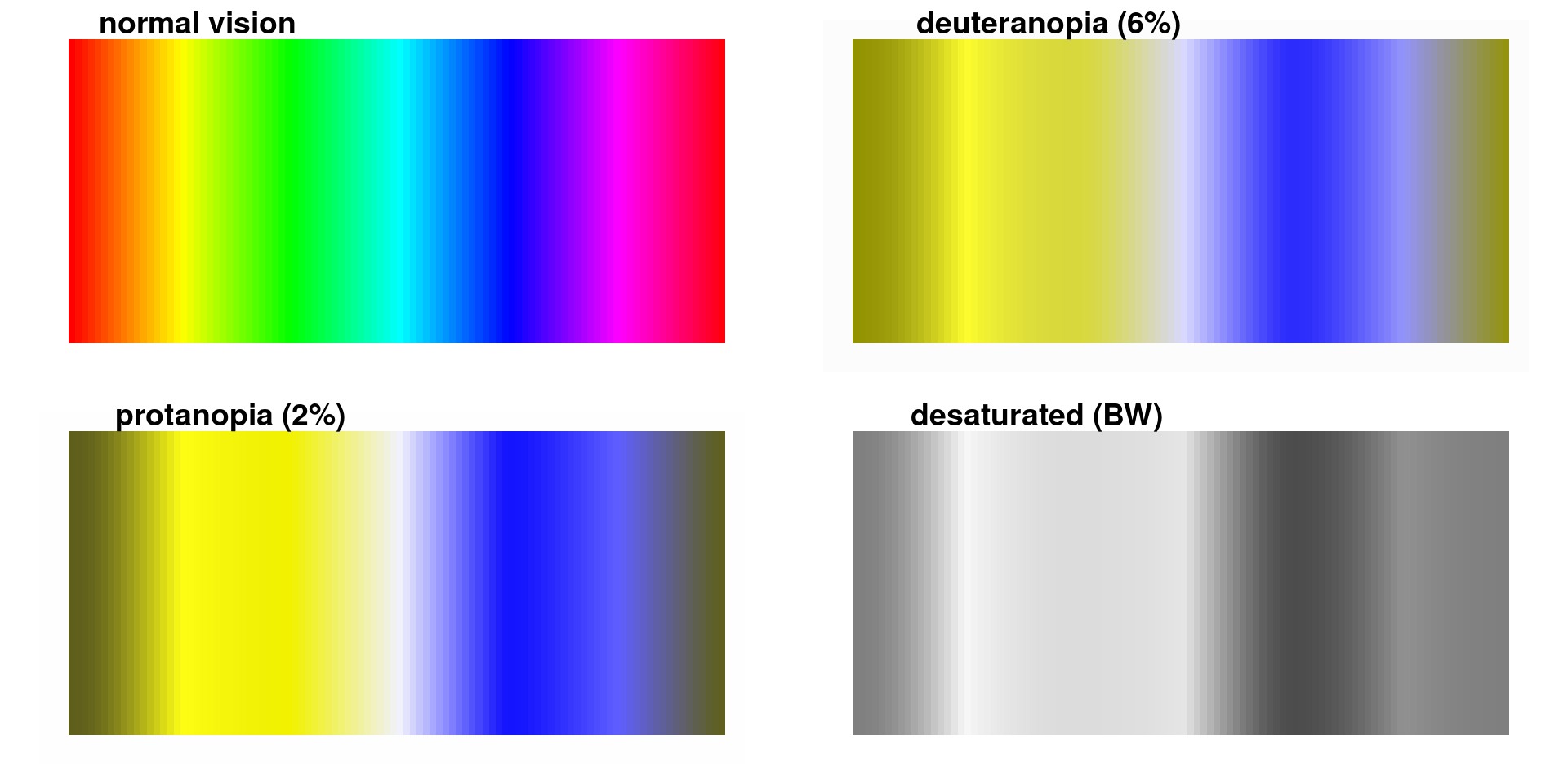

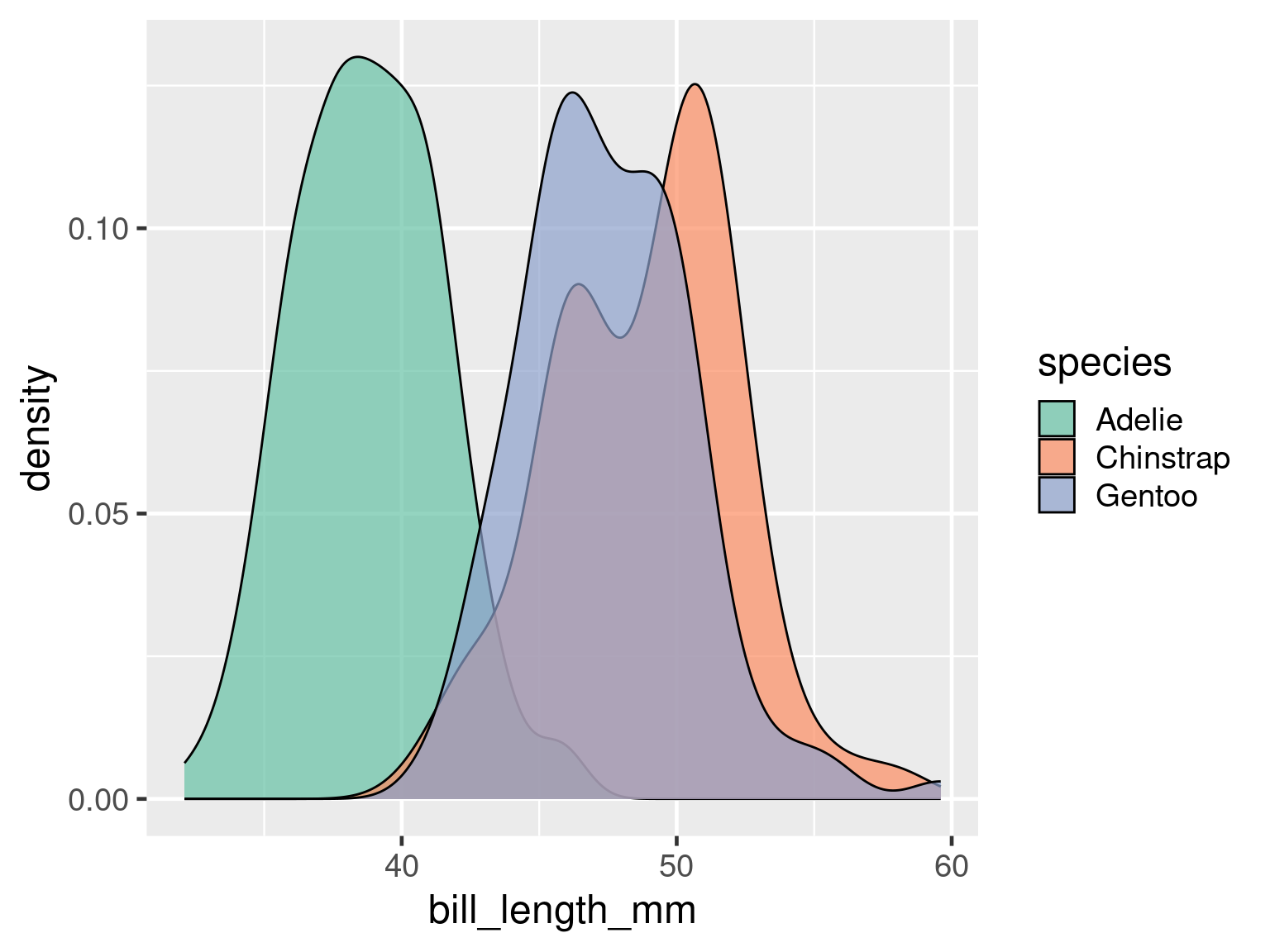
Better colour scale
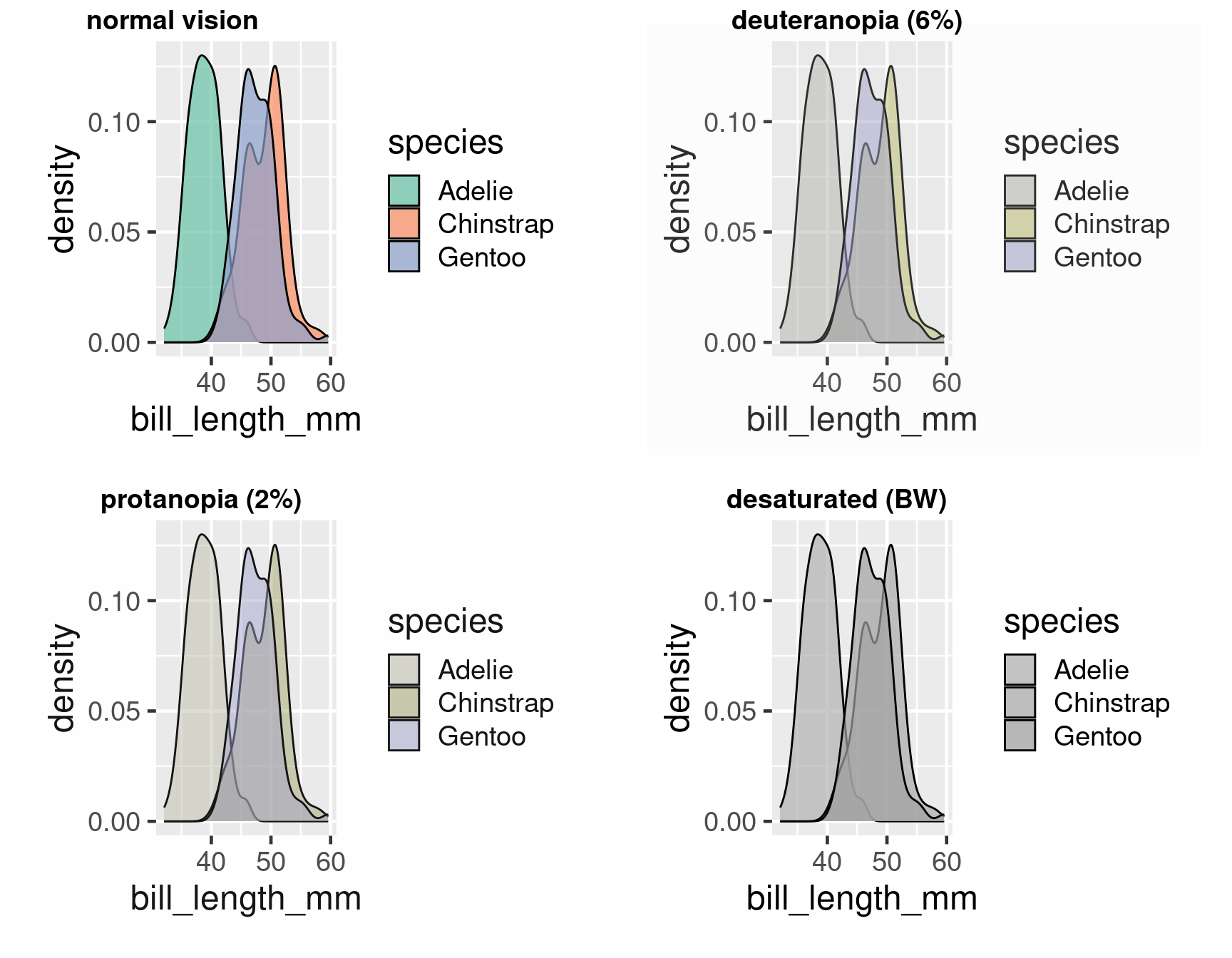
Using colour effectively
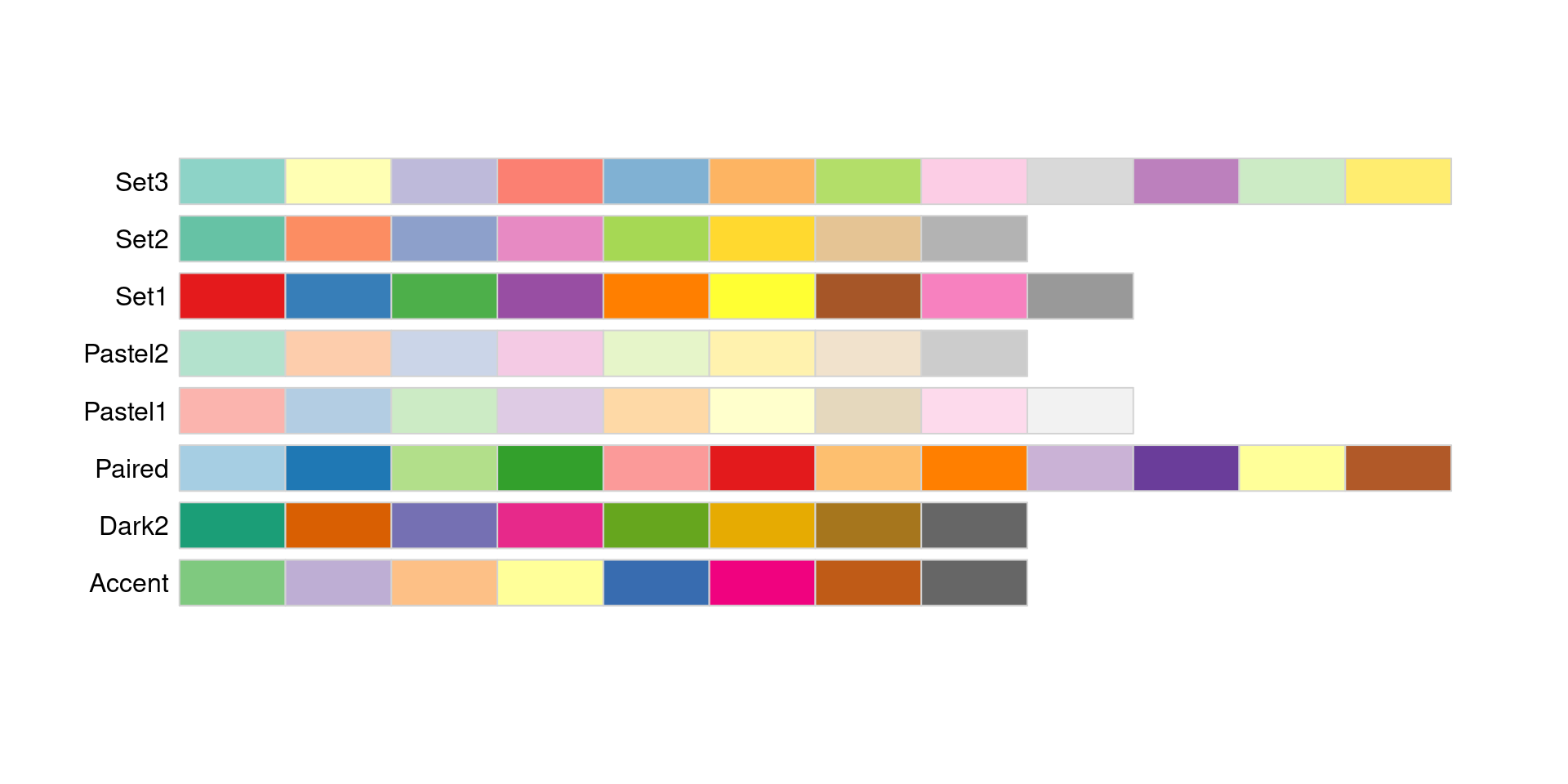
Choose an appropriate palette.
Qualitative palettes

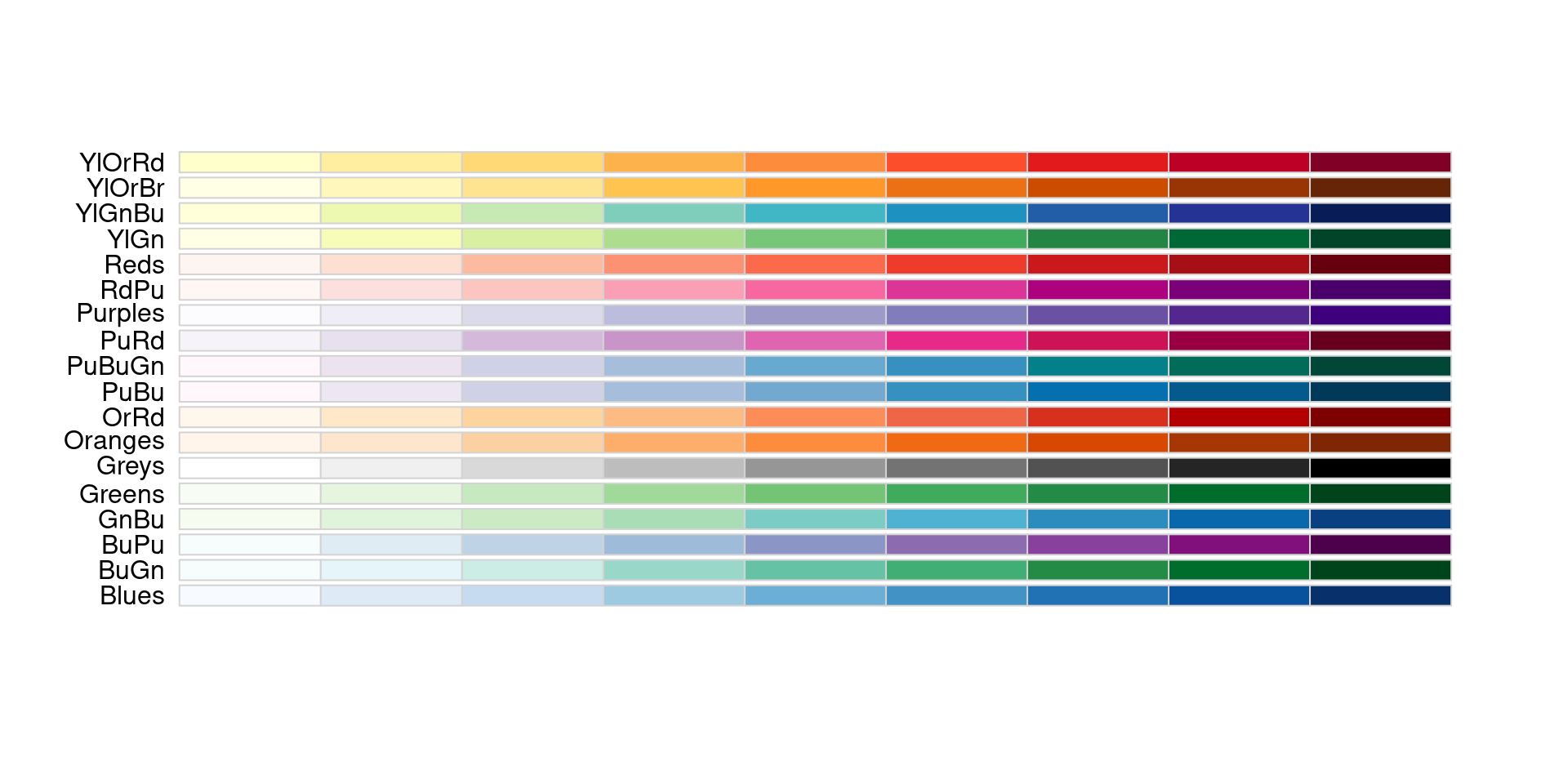
Sequential palettes

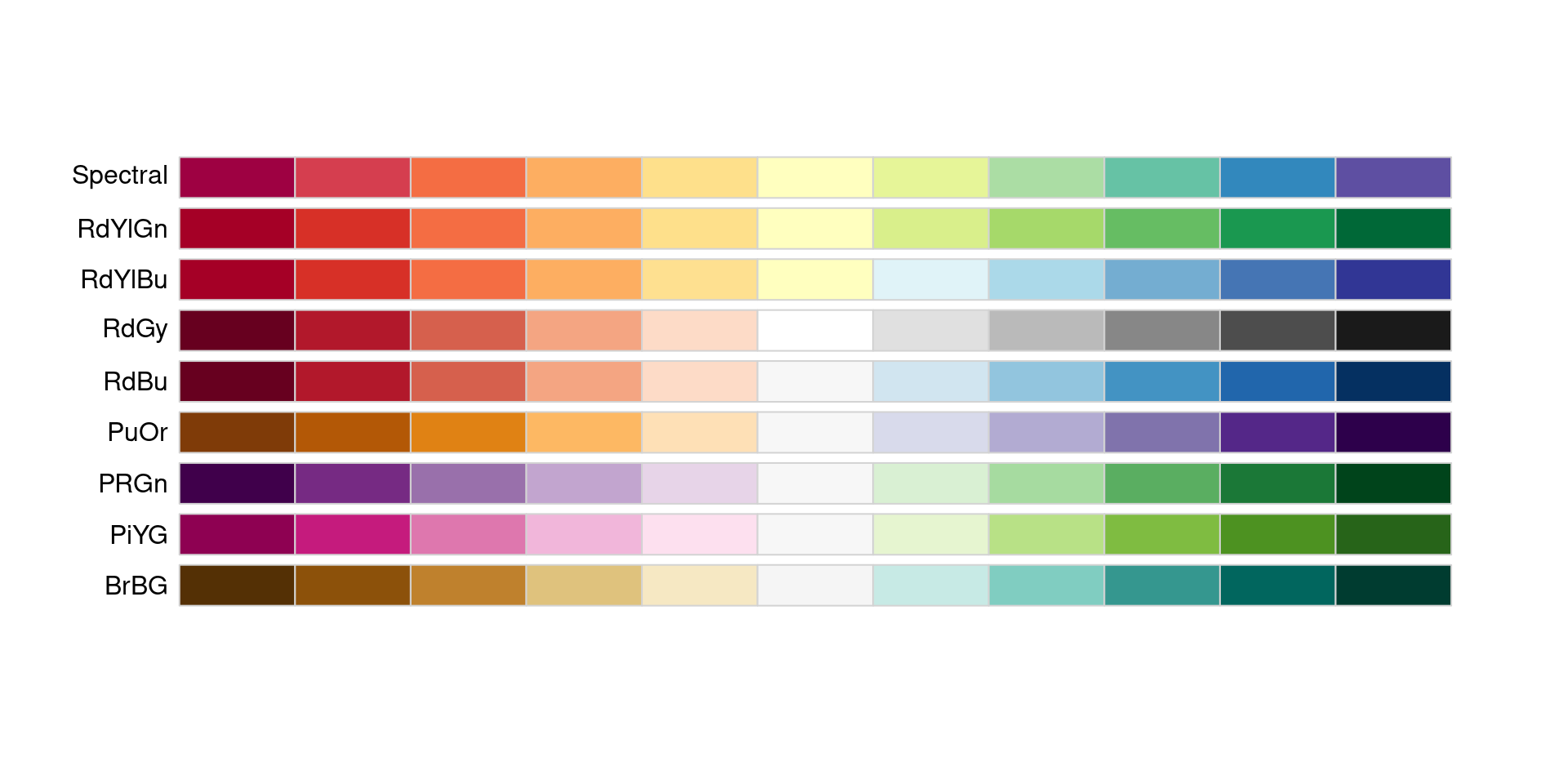
Dividing palettes

Viridis
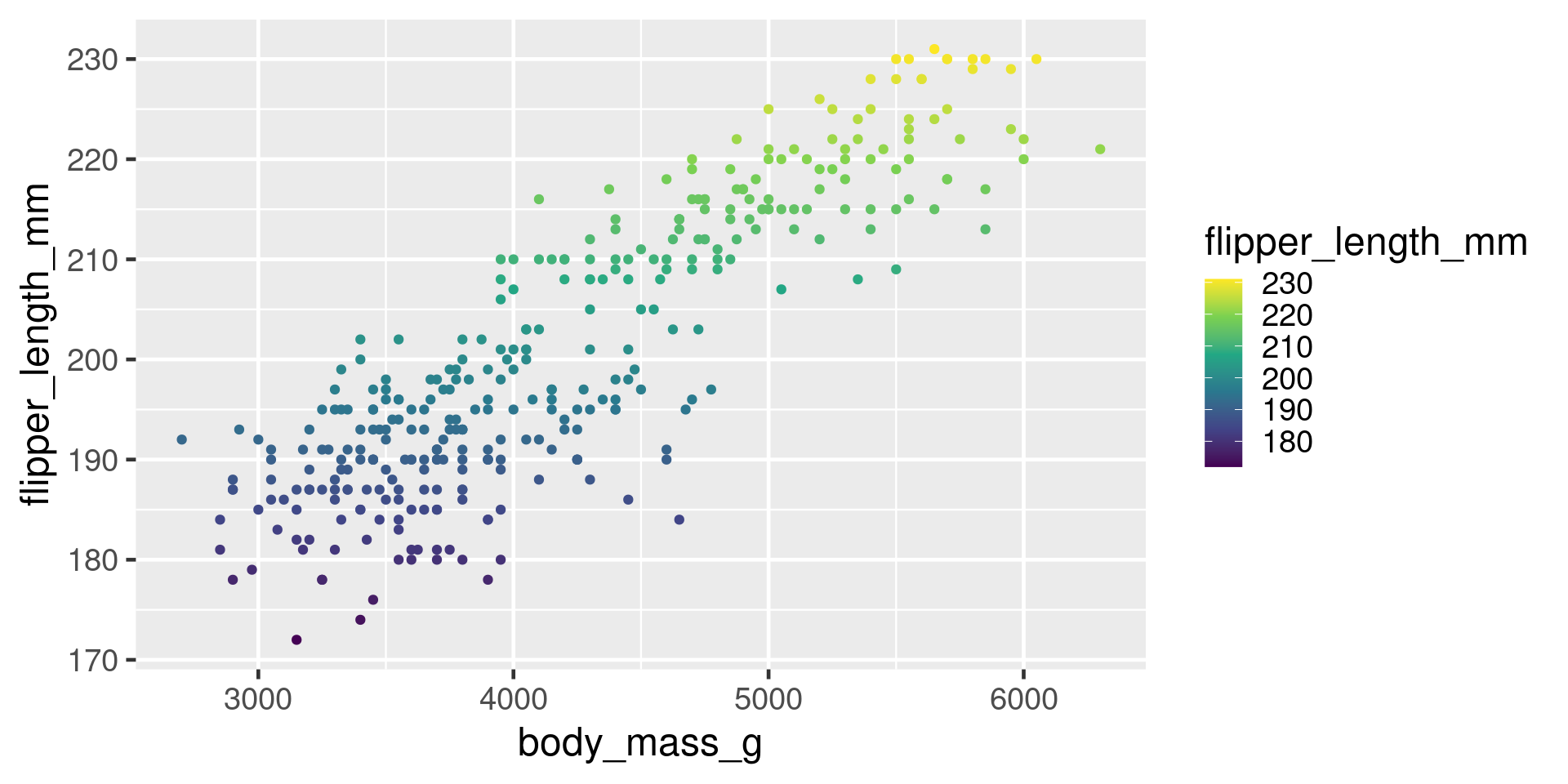
Highlight
Redundant encoding
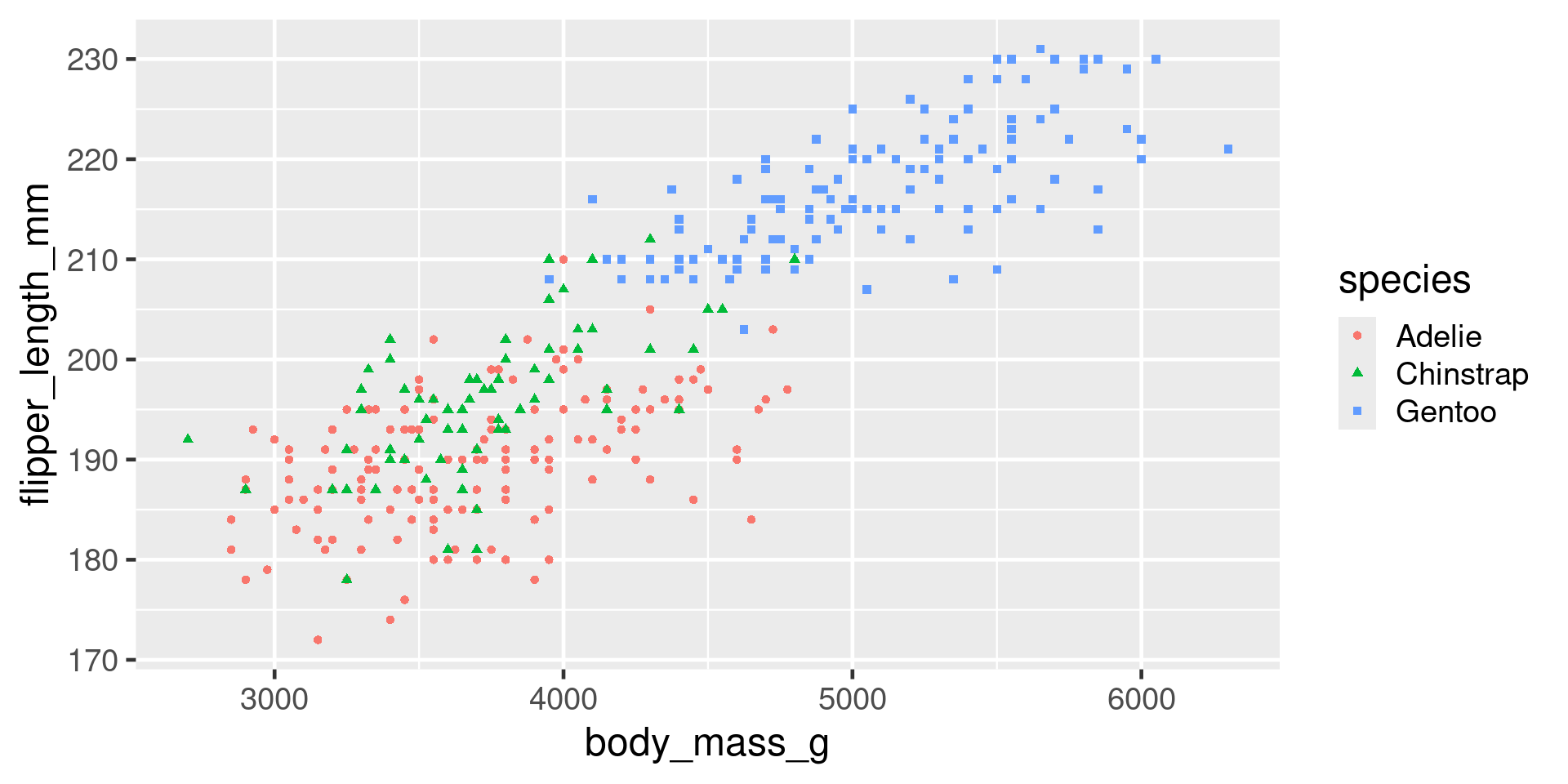
Also colour and linetype/linewidth
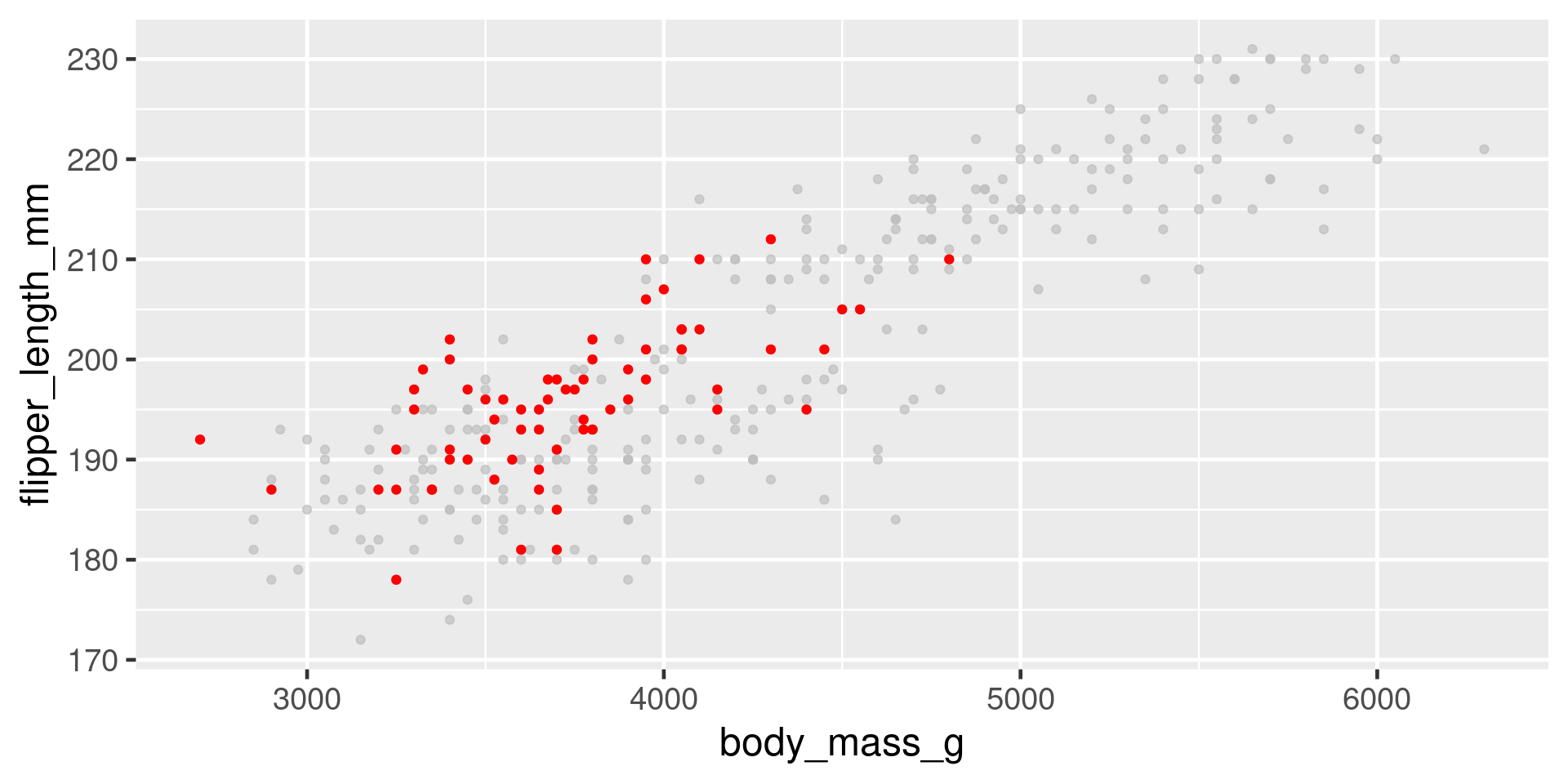
Avoiding legends
Avoiding overplotting
Problem - points plot on top of each other.
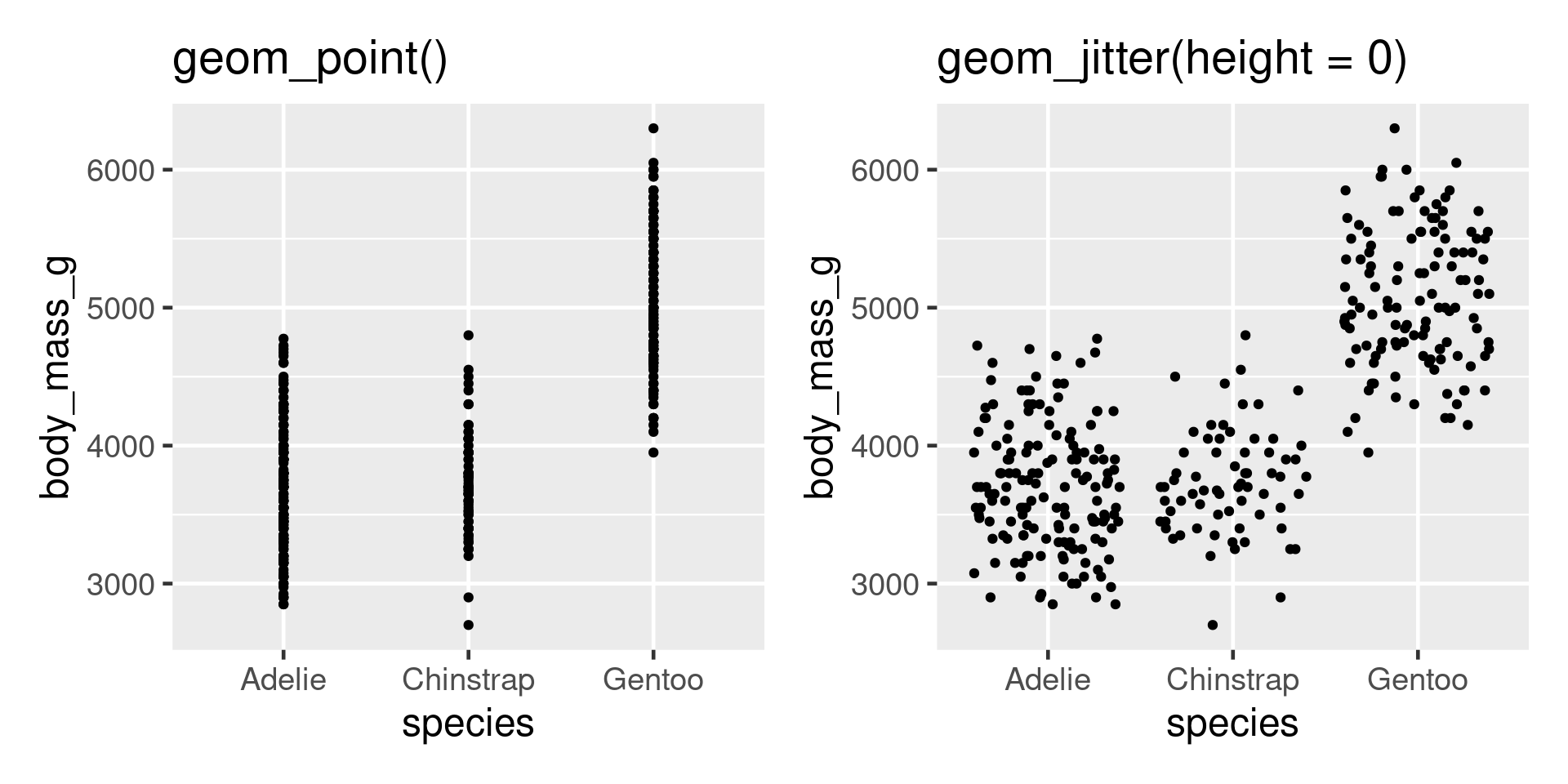
More overplotting
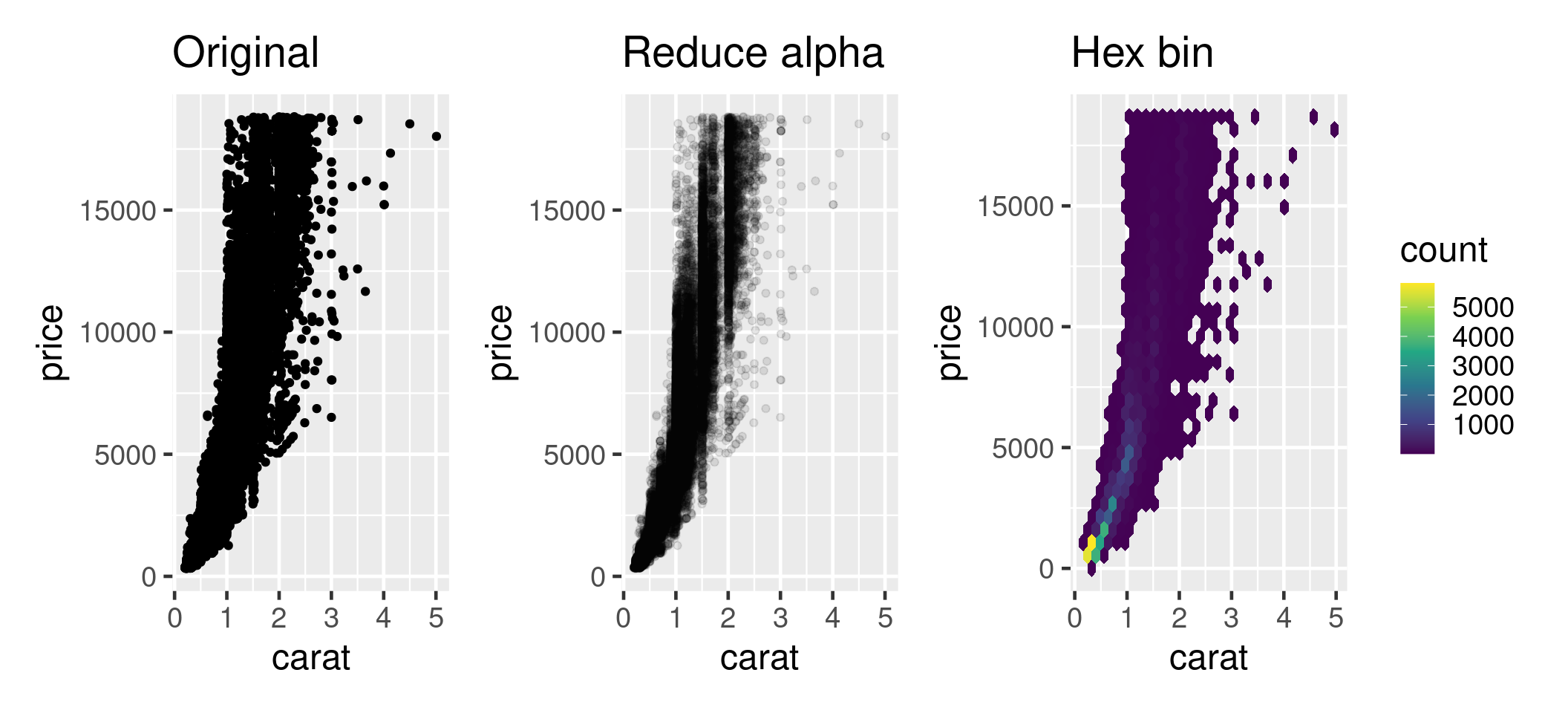
Problem - too much data
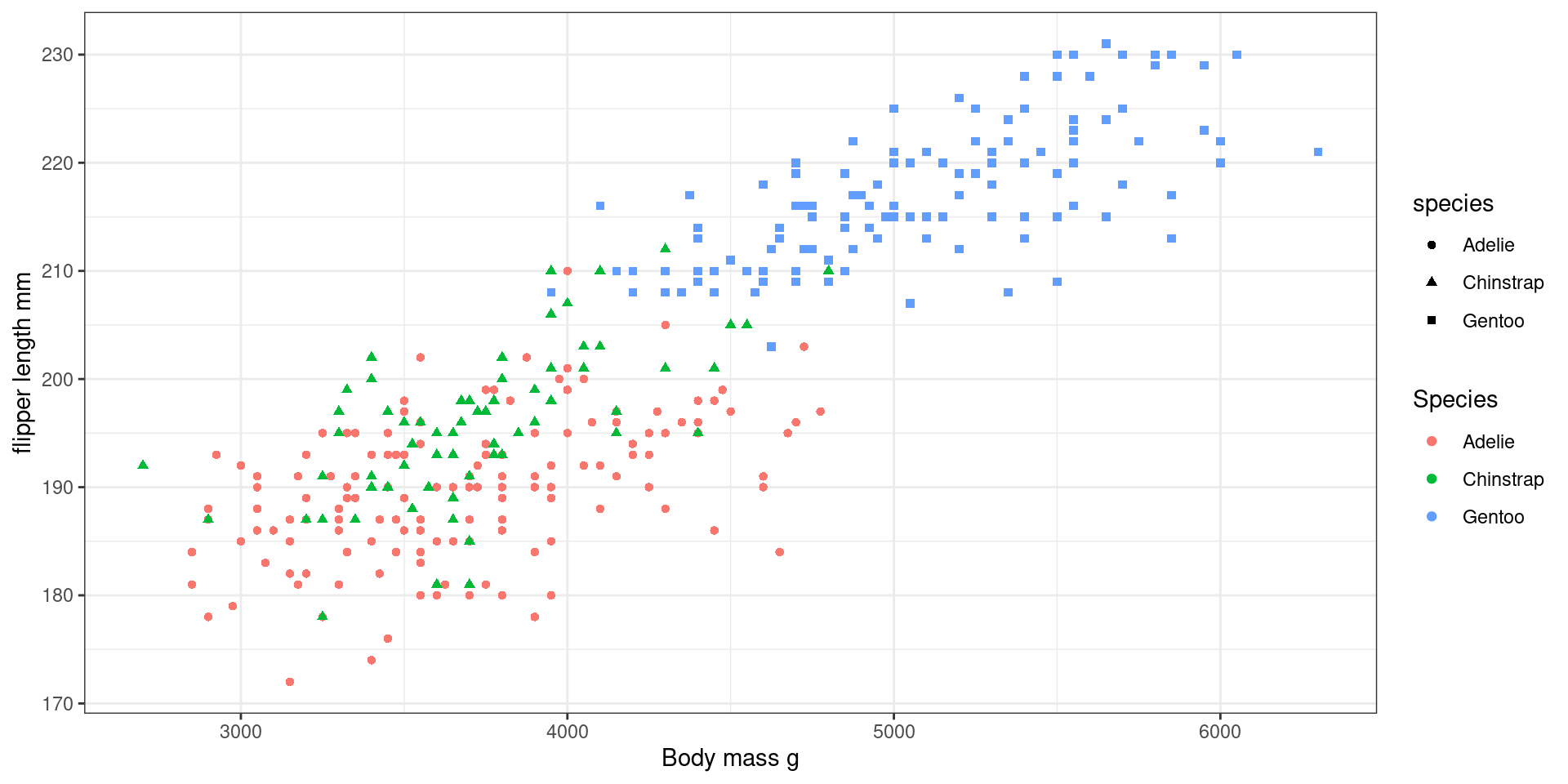
Most common mistake in presentations
Summary
- If you can imagine it, you can plot it
- Whole ecosystem of packages to help
Further reading
ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (3e) Wickham, Navarro, and Pedersen.