Version Control with Git and GitHub
1 Why use Git and GitHub?
Git is a version control system, which manages the evolution of files. GitHub is a online tool using the software git to store files and track changes. GitHub can be used with any files but works best with text files, for example R scripts. Here we will focus on installing and using git and GitHub with RStudio and explain the basic workflow..
Git and GitHub are widely used in industry and academia (put it on your CV). There are many ways to use git and GitHub. You can
use GitHub to host a webpage, perhaps one written with Quarto as this book is.
use the GitHub’s issues and discussion features for project management.
search GitHub for examples of how to use a function
use GitHub for publishing code
use git and GitHub to collaborate
use git and GitHub for version control of files.
The last two points are the main focus of this book.
1.1 Version control?
Version control makes it is easy to share code, collaborate on the same project, and keep track of all the changes in your code.

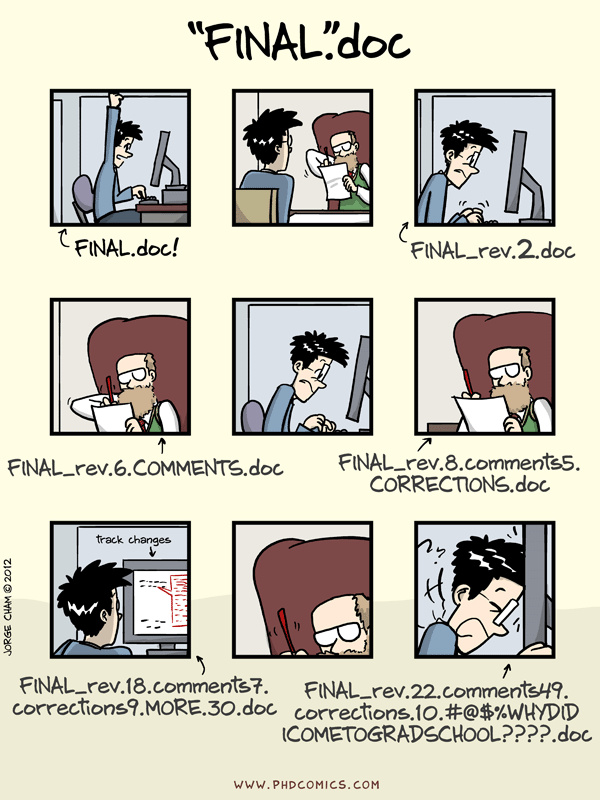
The graduate student in Figure 1.1 will likely struggle to identify which is the latest version of the file, what was changed between each version, and why the change was made.
Version control solves these problems. We make a snapshot of the state of one or more files, and make a message describing what changed. We can use version control to “time-travel” to an earlier version of our work, perhaps to identify bugs in the code.
Git is by far the most widely used system for version control. Other systems, such as Subversion, are little used any longer.
There are alternatives to GitHub, such as GitLab and bitbucket. These offer similar services with both free and paid plans. GitHub is the most popular and the tools used in this tutorial have been optimised for GitHub.
An increasing number of journals now expect you to archive the code used in your analyses when you publish a paper. GitHub is not suitable archive, because an unscrupulous scientist could simply delete the code after publication.
Instead, you should use a read-only file archive, such as figshare or zenodo, both of which can import code directly from GitHub.
GitHub is not a great place to archive data. It can be convenient to store small, unchanging files files there, but large or regularly updated files should be stored in a dedicated data archive such as osf or figshare.
Figshare, zenodo, or a discipline specific repository should be used when the manuscript is published. Bergen University Library has more information on how to archive data.
- git - version control software
- version control - a system for keeping snapshots of your work
- GitHub - one of several cloud-based systems for working with git
